News & Notes
The Blog ofMID-CONTINENT STEEL AND WIRE
The construction industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the integration of innovative technologies and materials that enhance efficiency, durability, and sustainability. Among these advancements, building materials steel stands out as a pivotal component in modern architecture and engineering. Known for its remarkable strength, flexibility, and recyclability, steel is not just a traditional choice but a revolutionary one that meets the demanding requirements of contemporary structures. This article explores the various ways steel is reshaping the landscape of construction, examining its applications in creating resilient buildings, its role in sustainable development, and how it compares to other materials in terms of performance. By embracing building materials steel, the construction sector is not only enhancing its capabilities but also paving the way for future innovations that align with the global shift towards smarter and greener building practices.
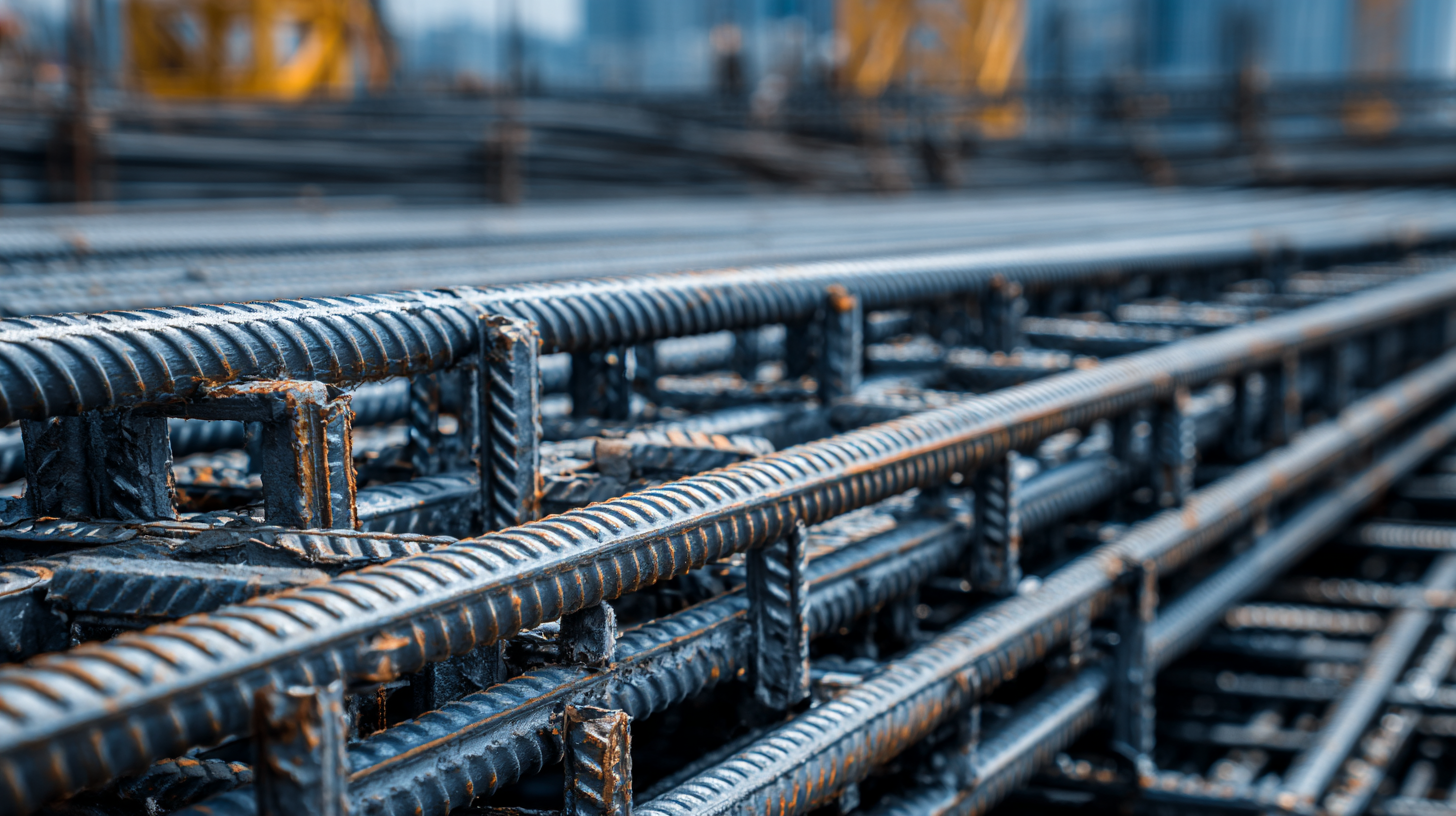

Steel has emerged as a vital component in modern construction, primarily due to its unique properties that cater to the evolving demands of the industry. As highlighted in the World Steel Association report, steel provides high tensile strength and durability, which allows for innovative designs with thinner structures while maintaining safety and stability. This adaptability can be seen in skyscrapers and expansive bridges, where a reduction in weight without sacrificing integrity is crucial. Buildings utilizing steel frames can reach heights previously deemed impossible, showcasing steel's essential role in architectural advancements.

Moreover, steel is inherently sustainable, which aligns with the growing focus on eco-friendly construction practices. According to a study by the American Iron and Steel Institute, steel is the most recycled material globally, with over 85% of structural steel being recycled after its lifecycle, thus minimizing waste and promoting circular economy principles. The energy-efficient production methods and longevity of steel structures further enhance its appeal, as they contribute to lower overall carbon footprints in comparison to traditional building materials. With these characteristics, steel not only revolutionizes construction methods but also supports a sustainable future for the industry.
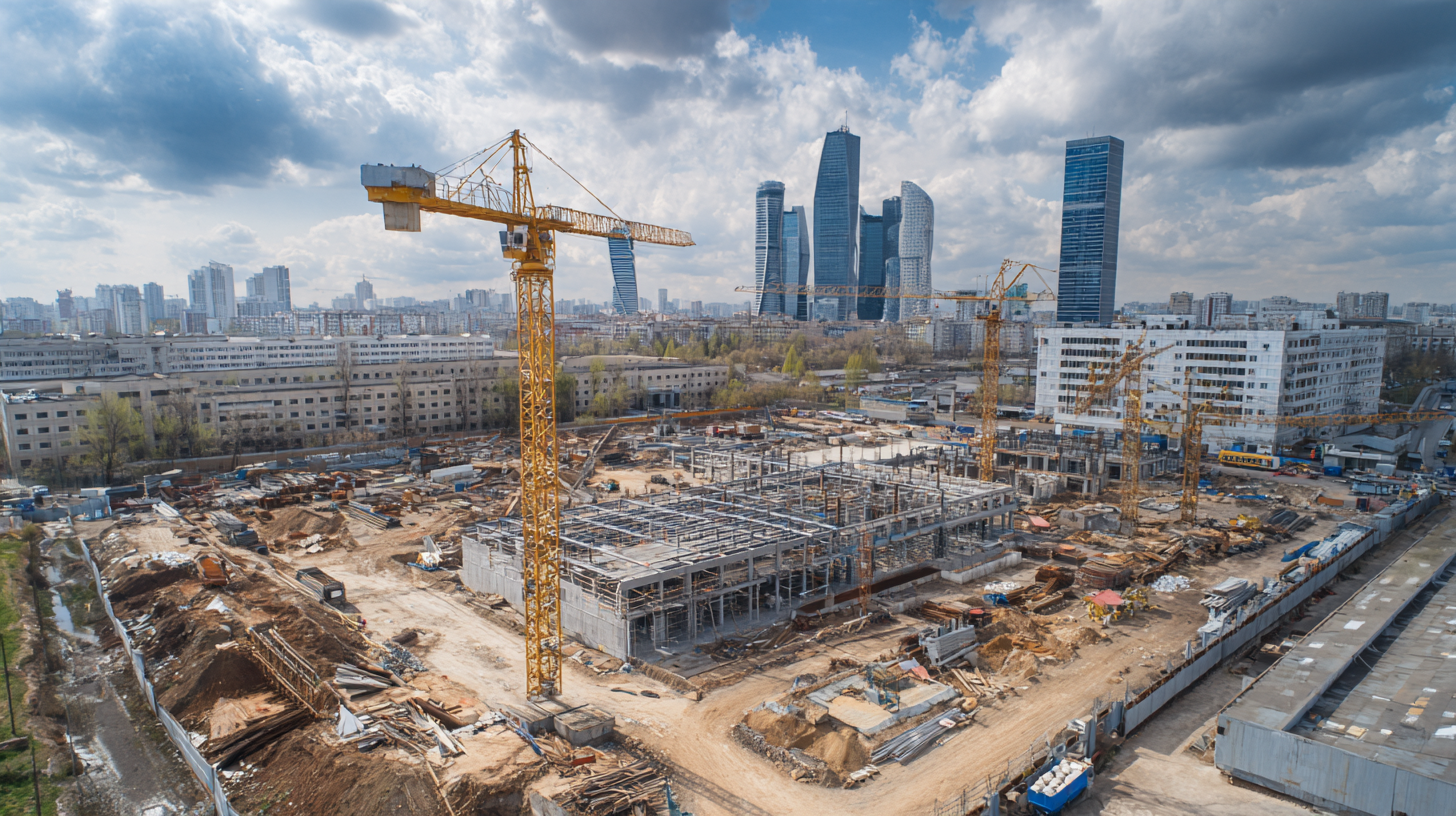
The demand for innovative uses of steel in sustainable building practices is rapidly accelerating, particularly in the non-residential sector. With a predicted compound annual growth rate of 4.12%, the prefabricated structural steel market is poised to reach a valuation of approximately $203.6 billion by 2032. This growth is largely fueled by the increasing need for cold storage facilities, industrial buildings, and institutional structures. As sustainability becomes a central focus in construction, the material properties of steel—such as its recyclability and durability—make it an ideal choice for modern building practices.
Recent initiatives, such as the C40 Cities Visible project launched in 2023, aim to explore equitable and sustainable building methodologies in cities like Oslo, London, and Madrid. These programs signify a broader trend towards integrating advanced technologies in construction, including automation and digitalization, which further enhance the sustainability of steel as a construction material. By leveraging innovative steel applications, the construction industry can contribute significantly to achieving zero carbon building practices, affirming steel's role in the future of sustainable architecture.
In recent years, the construction industry has seen a significant shift towards the use of steel, especially when compared to traditional building materials like wood, concrete, and brick. A report from the World Steel Association indicates that steel is both lighter and stronger than many traditional materials, often leading to reduced material usage and lower transportation costs. For instance, steel's high strength-to-weight ratio allows for longer spans in structural frameworks, offering greater flexibility in design and maximizing the use of floor space.
Additionally, the environmental impact of steel in construction is noteworthy. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), steel production has become increasingly efficient, with advancements resulting in a 30% reduction in emissions per ton of steel produced over the last two decades. In comparison, traditional materials like concrete contribute significantly to greenhouse gases, accounting for approximately 8% of global CO2 emissions. The recyclability of steel offers another advantage; over 85% of steel is recycled at the end of its life cycle, enhancing sustainability efforts and making it a preferred choice for modern building projects.
| Criteria | Steel | Traditional Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High | Moderate |
| Durability | Excellent | Variable |
| Cost | Higher Initial Cost | Lower Initial Cost |
| Construction Speed | Fast | Slower |
| Sustainability | Recyclable | Limited Recyclability |
| Fire Resistance | Good with Treatment | Variable |
In contemporary architecture, steel has emerged as a fundamental building material that shapes modern design trends. Its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio allows architects to explore innovative structural forms that were previously unattainable with traditional materials. From towering skyscrapers to elegant bridges, the flexibility of steel enables the creation of expansive open spaces and intricate designs, embodying the spirit of modernism. The use of exposed steel beams and frameworks not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also celebrates the industrial essence of construction, giving buildings a unique character.
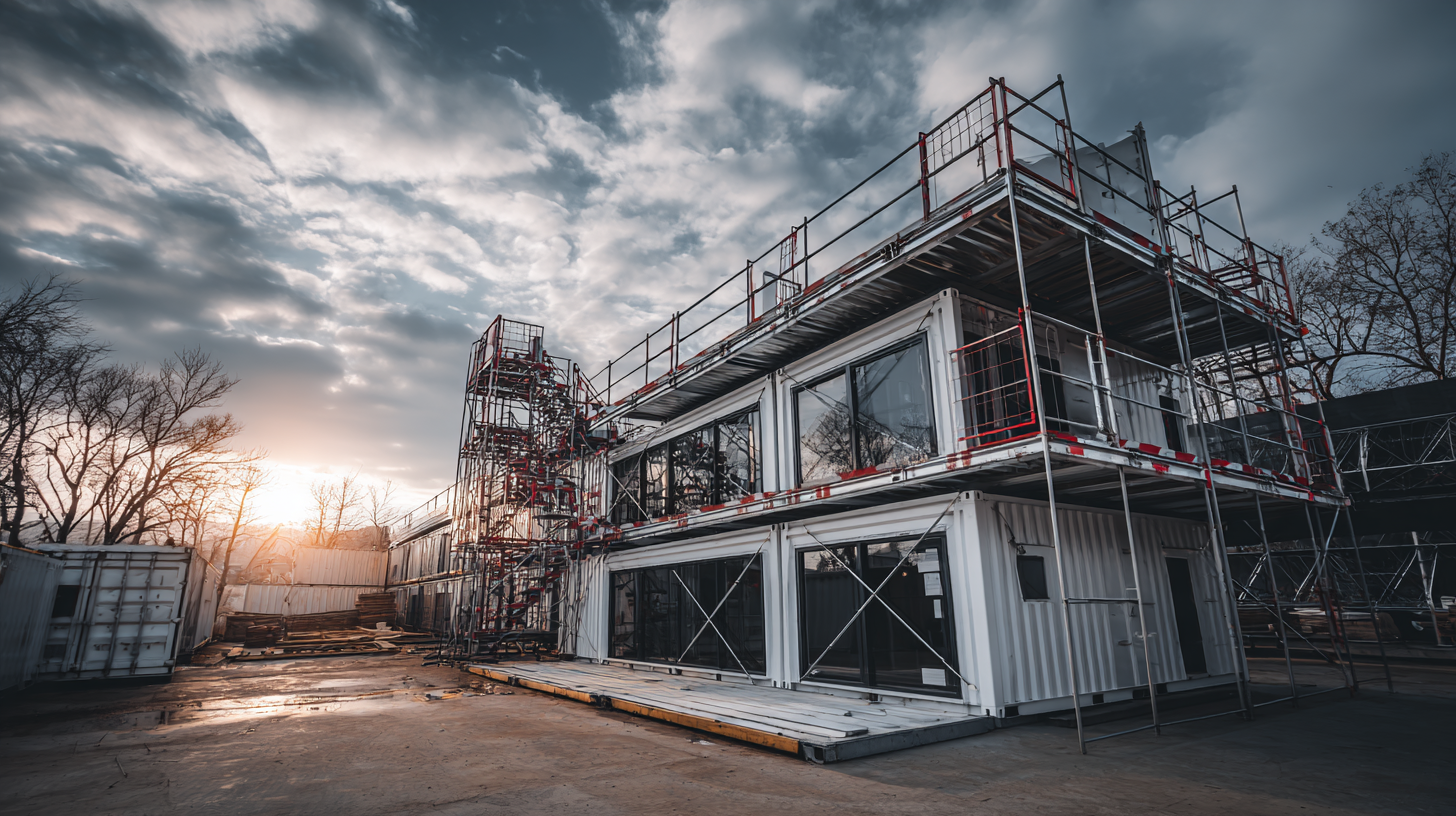

Additionally, the sustainability movement in architecture has further propelled the use of steel in design. Steel is highly recyclable, reducing the environmental impact associated with construction. Modern buildings often incorporate steel in hybrid designs, integrating it with other materials like glass and timber to achieve a harmonious balance between durability and visual warmth. This approach not only emphasizes functionality but also promotes energy efficiency, as steel components can be manufactured and assembled with precision, leading to reduced waste. As architects continue to embrace these trends, the role of steel in shaping the future of architecture becomes increasingly vital.
Advancements in steel technology are set to revolutionize housing solutions, driving increased efficiency and sustainability in the construction industry. Innovations such as high-strength steels and corrosion-resistant coatings are being developed to improve the durability and lifespan of structures while reducing maintenance costs. These materials not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of buildings but also allow for greater design flexibility, enabling architects to create unique and creative forms that were previously difficult to achieve.
Moreover, the integration of smart technologies into steel manufacturing represents a significant leap forward. Techniques like 3D printing and automated fabrication are optimizing production processes, decreasing waste, and further lowering the carbon footprint associated with building construction. As steel continues to evolve, its role in modern building materials will increasingly align with the industry's move toward sustainability, offering eco-friendly alternatives that meet the growing demand for affordable and efficient housing solutions in urban environments.





If you need more information about our products or you can’t find what you are looking for, please reach us via our contact form and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
© 2022 MID-CONTINENT STEEL AND WIRE, ALL RIGHTS RESERVED | PRIVACY POLICY | PRIVACY POLICY – CALIFORNIA